Life Process -Human and Animal Life Process Hindi or English
Life Process -Human and Animal Life Process
Hindi or English
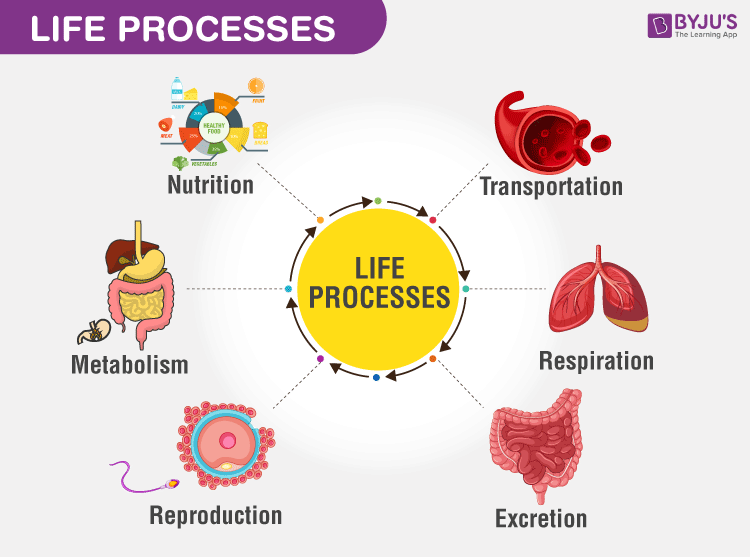
Life forms(Process )– The procedures that are fundamental for a life form to remain alive. Eg. Nutrition,respiration, and so forth.
➣ Criteria of life-(I) Growth (ii) Movement
➣ Nutrition-The procedure wherein a creature takes in food, uses it to get energy, for development, fix and support, and so on and discharges the waste materials from the body
जीवन रूप (प्रक्रिया) - वे प्रक्रियाएँ जो जीवन रूप बने रहने के लिए मौलिक हैं। उदाहरण के लिए। पोषण, श्वसन और इसके बाद।
➣ जीवन का मापदंड- (I) विकास (ii) आंदोलन
➣ पोषण-वह प्रक्रिया जिसमें कोई प्राणी भोजन में लेता है, इसका उपयोग ऊर्जा प्राप्त करने के लिए करता है, विकास के लिए, ठीक करने और समर्थन करने के लिए, और इसी तरह शरीर से अपशिष्ट पदार्थों को बाहर निकालता है।
Hindi or English
Life forms(Process )– The procedures that are fundamental for a life form to remain alive. Eg. Nutrition,respiration, and so forth.
➣ Criteria of life-(I) Growth (ii) Movement
➣ Nutrition-The procedure wherein a creature takes in food, uses it to get energy, for development, fix and support, and so on and discharges the waste materials from the body
जीवन रूप (प्रक्रिया) - वे प्रक्रियाएँ जो जीवन रूप बने रहने के लिए मौलिक हैं। उदाहरण के लिए। पोषण, श्वसन और इसके बाद।
➣ जीवन का मापदंड- (I) विकास (ii) आंदोलन
➣ पोषण-वह प्रक्रिया जिसमें कोई प्राणी भोजन में लेता है, इसका उपयोग ऊर्जा प्राप्त करने के लिए करता है, विकास के लिए, ठीक करने और समर्थन करने के लिए, और इसी तरह शरीर से अपशिष्ट पदार्थों को बाहर निकालता है।

Kinds of nutrition :-
1. Autotrophic nutrition (Auto =self: trophos = sustenance)
Life Processes of Plants and Human Life
E.g. Plants, Algae, blue green microbes.
# Process – Photosynthesis (Photo=light; Synthesis= to join)
# Raw materials-(I) Carbon dioxide (ii)Water
पोषण के प्रकार: -
1. ऑटोट्रॉफ़िक पोषण (ऑटो = स्व: ट्रोफ़ोस = जीविका)
पौधों और मानव जीवन की जीवन प्रक्रियाएं
जैसे पौधे, शैवाल, नीले हरे रोगाणु।
# प्रक्रिया - प्रकाश संश्लेषण (फोटो = प्रकाश; संश्लेषण = जुड़ने के लिए)
# कच्चा माल- (I) कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड (ii) पानी
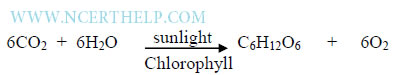 # Equation-
# Equation-Autotrophic nutrition :-
# Energy transformation Light/Solar energy to Chemical energy
# Role off Chlorophyll-To trap the sun's energy for photosynthesis
#Factors for Autotrophic nutrition -
(I) Carbon dioxide
(ii) Water
(iii) Light
(iv) Temperature
ऑटोट्रॉफ़िक पोषण: -
# ऊर्जा परिवर्तन लाइट / सौर ऊर्जा को रासायनिक ऊर्जा
# प्रकाश संश्लेषण के लिए क्लोरोफिल-से सूर्य की ऊर्जा को फँसाना
ऑटोट्रॉफ़िक पोषण के लिए #Factors -
(I) कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड
(ii) पानी
(iii) प्रकाश
(iv) तापमान
# Events/Steps of photosynthesis :-
(I) Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll
(ii) Conversion of light energy to compound energy and Splitting of water particle into Hydrogen and oxygen
(iii) Reduction of Carbon dioxide to Carbohydrate
#Gaseous trade
(I) Gas utilized Carbon dioxide
(ii) By item - Oxygen
# Source of crude materials-
(I) Carbon dioxide – Land plants-Air, Aquatic plants-Water
(ii) Water and Minerals - Soil
2. Heterotrophic nutrition (Hetero =others: trophos =ourishment)
Eg. Creatures, plants lacking chlorophyll like organisms.
..
(a) Saprophytic nutrition: Organisms b..enefits from dead rotting plants or creatures material. For example Parasites, Bacteri
(b) Parasitic nutrition: Organisms acquire food from the body of another living (have)
o Endoparasite : Parasite lives inside the body of the host for example tapeworm, roundworm.
o Exoparasite : Parasite lives on the body of the host. For example lice, siphon.
Note-The parasite benefits while the host is generally hurt for example Cuscutta-plant parasite (amar bel), plasmodium (malarial parasite).
(c) Holozoic nutrition: Organism (generally creatures) take in entire food and afterward digest it into littler particles with protein. Eg.Amoeba, Paramoecium. Creatures, individuals.
Steps in Holozoic nutrition:-
(I) Ingestion: taking in of food.
(ii) Digestion: separating of complex food into less difficult, absorbable structure.
(iii Assimilation: Utilization of processed food from the body.
(iv)Egestion: Removing undigested food from the body
Nutrition in individuals:-
♦ Alimentary trench
Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small digestive system Large digestive tract
♦ Important organ/juices
Organ
Organ
Catalyst/Juice
Capacity
Mouth
Salivary
organs
Salivary Amylase
Changes over starch into sugar
Stomach
Gastric organs
Gastric juice:-
(I) Hydrochloric
corrosive
(a) Kills unsafe microscopic organisms that enters with the food.
(b) Makes the medium antacid for the activity of Pepsin
(ii) Pepsin
Summaries proteins
(iii) Mucus
Ensures the internal covering of the stomach from the destructive activity of Hydrochloric corrosive.
Digestive system:-
1) Liver
(I) Bile juice
(a) Makes the medium acidic
for the activity of Pancreatic compounds.
(b) Breaks down enormous fat atoms into littler globules with the goal that catalysts can follow up on them.
2) Pancreas
( ii) Pancreatic
Juice
♦ Amylase
Changes over Carbohydrates to glucose
♦ Trypsin
Changes over Proteins to Amino acids
♦ Lipase
Changes over Fats into Fatty acids and Glycerol
Oxygen consuming espiration
Anaerobic breath
1. Takes place in nearness of Oxygen.
2. Final results Carbon dioxide and Water
3. More energy is discharged.
4. Takes place in Cytoplasm and Mitochondria
5. Complete oxidation of glucose takes place.
6. It happens in many life forms.
7. Condition
Glucose→ Pyruvate→ CO2 + H2O + Energy
1. Takes place without Oxygen.
2. Final results Ethanol and Carbon dioxide
3. Less energy is discharged.
4. Takes place in just in Cytoplasm.
5. Deficient oxidation of glucose takes place.
6. It happens in specific microbes, yeast and certain tissues of higher creatures. For example In people during enthusiastic exercise, when the interest for Oxygen is more than the inventory, muscle cells breathe anaerobically for quite a while.
7. Condition In Yeast-
Glucose→ Pyruvate→ Ethanol + H2O + Energy
In muscle cells - Glucose→ Pyruvate→ Lactic corrosive + Energy
o Some basic highlights of Respiratory organs-
(I) Large surface territory for more noteworthy pace of dissemination of respiratory gases.
(ii) Thin porous dividers – to guarantee simple dissemination and trade of gases.
(iii) Extensive blood supply-Respiratory organs are luxuriously provided with blood vessels for snappy vehicle of gases.
o Gaseous trade in plants:-
♦ Process – Diffusion
♦ Direction of dissemination relies upon
(I) Environmental conditions
(ii) Requirement of the plant.
♦ Day time-Carbon dioxide given out during breath is utilized for photosynthesis.Therefore just Oxygen is discharged, which is a significant movement during the day.
♦ Night time – Only breath takes place. Along these lines just Carbon dioxide is discharged, which is a significant movement during the night.
o Gaseous trade in creatures:-
♦ Terrestrial creatures take Oxygen from the air.
♦ Aquatic creatures take Oxygen broke up in water. (Oxygen content is low in water, along these lines they inhale quicker.
o Human Respiratory framework
Outer nostrils → Nasal pit → Trachea→ Bronchi → Bronchioles →Alveoli
♦ Rings of ligament present in the throat guarantee that the trachea (air section) doesn't fall when there is less air in it.
♦ Lungs: –
(I) Present in the thoracic cavity.
(ii) They are light, versatile packs comprising of Bronchi, Bronchioles and Alveoli
Allude to figure 6.9 page no. 104 of N.C.E.R.T Text book)
o Respiration happens in two stages:-
(I) External-Breathing, which is a mechanical procedure.
(ii) Internal - Cellular breath
o Mechanism of breathing – It incorporates :
(i)Inhalation
(ii) Exhalation
o Exchange of gases:-
♦ Unicellular living beings By Diffusion
♦ Animals-
(I) As the body size is enormous, dispersion alone isn't sufficient.
(ii) Respiratory shades additionally required.
(iii) Respiratory shade in people is Hemoglobin, which is available in red blood corpuscles.
(iv) It has exceptionally high liking for Oxygen.
(iv) Carbon dioxide is more solvent in water than Oxygen, so it
Gets breaks down in blood and is therefore moved.
v Transportation
Transportation in individuals
♦ Blood-
(I) It is a liquid connective tissue.
(ii) Components-
(1) Fluid medium-Plasma (2) Red blood corpuscles (3) White blood corpuscles
(4) Platelets suspended in plasma
(iii) Plasma transports food, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Nitrogenous squanders, and so forth.
♦ Functions of blood:-
(I) Transport of respiratory gases.
(ii) Transport of supplements.
(iii) Transport of waste items.
(iv) Defense against contamination
♦ Blood vessels-(I) Arteries (ii) Veins (iii) Capillaries
Veins:-
1. Thick walled.
2. Profound situated.
3. Divert blood from the heart.
4. Convey Oxygenated blood.
5. Valves missing.
1. Slim walled.
2. Shallow.
3. Convey blood to the heart.
4. Convey Deoxygenated blood.
5. Valves present
♦ Heart-
(Allude to figure 6.10 page no. 106 of N.C.E.R.T Text book)
(I) It is a strong organ, which fills in as a siphon in the circulatory framework.
(ii) It is the size of our clench hand.
(iii) It has different sides, which are isolated by a segment so that the oxygenated and deoxygenated blood don't get stirred up.
(iv) It has four chambers-
Two upper chambers called Atria.
Two lower chambers called Ventricles.
♦ Working of heart-Left side-
(I) Left chamber unwinds and the Oxygenated blood enters it from the lungs through the aspiratory vein.
(ii) Left chamber contracts and the blood enters the left ventricle through the valve.
(iii) Left Ventricle contracts and the blood is siphoned into the
biggest vein ‗Aorta' and is conveyed to all pieces of the body.
♦ Working of heart-Right side-
(I) Right chamber unwinds and the deoxygenated blood from the body enters it through predominant and substandard Vena cava.
(ii) Right chamber contracts and the blood enters the correct Ventricle through the valve.
(iii) Right Ventricle contracts and the blood is siphoned into the Pulmonary supply route and is conveyed to lungs.
♦ Valves-Unidirectional to forestall the regressive progression of blood.
♦ Pulmonary vein is the main vein that conveys Oxygenated blood.
♦ Aorta is the main course that conveys Deoxygenated blood.
♦ Double flow in man-in light of the fact that the blood goes through the heart twice in one complete pattern of the course.
♦ Capillaries-
(I) Form the association between supply routes and veins.
(ii) Walls are one cell thick just for simple trade of blood.
♦ Platelets-Plug the holes of conduits and veins by thickening the blood.
♦ Lymph-Extracellular liquid like plasma however dry with lesser protein.
♦ Function of lymph-
(I) Transportation of processed and assimilated fats from the small digestive system.
(ii) Drains overabundance liquid from the intercellular spaces back in the blood.
♦ Higher creatures E.g., winged animals, well evolved creatures.
(i)Oxygenated blood and Deoxygenated blood are totally discrete for productive Oxygen supply.
(ii)This is to satisfy higher energy needs and to keep up internal heat level (warm blooded creatures).
♦ Amphibians and reptiles-have 3 chambered warmth where small blending of Oxygenated blood and Deoxygenated blood takes place. Accordingly their internal heat level changes
Comments
Post a Comment