Cache Memort in Computer
.Cache Memory.
Introduction:
Introduction:
Cach Memory is a temporary memory ,its make a copy for all material .
Cache memory cover some space.
Cache memory some prose and cones are available.
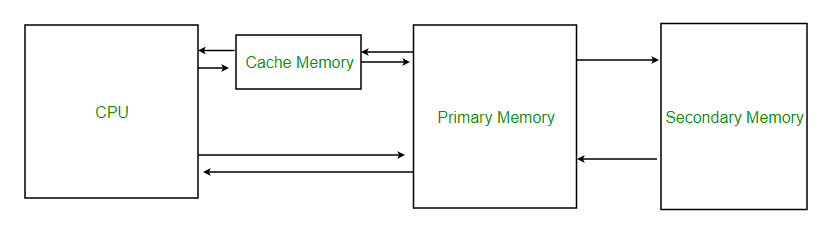
Its computer and Smart devices memory.
(1) To store data locally so as to speed up resulting recoveries. Articulated "money." See Web cache and program cache.
(2) Reserved zones of memory (RAM) in each PC that are utilized to speed up handling. Articulated "money," they fill in as rapid arranging zones that are continually loaded up with the next arrangement of guidelines or data. Caches have quicker information/yield than the regions that feed them. For instance, memory caches are rapid memory, which is quicker than main memory, and disk caches are main memory, which is quicker than disk.
(2) Reserved zones of memory (RAM) in each PC that are utilized to speed up handling. Articulated "money," they fill in as rapid arranging zones that are continually loaded up with the next arrangement of guidelines or data. Caches have quicker information/yield than the regions that feed them. For instance, memory caches are rapid memory, which is quicker than main memory, and disk caches are main memory, which is quicker than disk.
 Disk Caches :
Disk Caches :Memory Caches :
A memory cache, likewise called a "CPU cache," is a memory bank that extensions main memory and the processor. Including quicker static RAM (SRAM) chips than the dynamic RAM (DRAM) utilized for main memory, the cache permits guidelines to be executed and data to be perused and composed at higher speed. Guidelines and data are moved from main memory to the cache in fixed squares, known as cache "lines," utilizing a look-ahead calculation. See cache line, static RAM and dynamic RAM.
Worldly and Spatial (Time and Space) :
Caches exploit "worldly area," whereby perpetual data constants, for example, high-low cutoff points, messages and section headers are utilized again and again. Caches likewise advantage from "spatial area," in light of the fact that the next guidance to be executed or the next arrangement of data to be prepared is frequently next in line. The more consecutive they are, the more noteworthy the possibility for a "cache hit." If the next thing isn't in the cache, a "cache miss" happens, and it must be recovered from more slow main memory.
Levels 1, 2 and 3 (L1, L2, L3)
The present CPU chips contain a few caches, with L1 being the quickest. Each consequent cache is increasingly slow than L1, and directions and data are arranged from main memory to L3 to L2 to L1 to the processor. On multicore chips, the L3 cache is commonly shared among all the preparing centers. See compose back cache and compose through cache.
A disk cache is a committed square of memory (RAM) in the PC or in the drive controller that extensions stockpiling and CPU. At the point when the disk or SSD is perused, a bigger square of data is replicated into the cache than is quickly required. In the event that resulting peruses discover the data previously put away in the cache, there is no compelling reason to recover it from capacity, which is more slow to get to.
In the event that the cache is utilized for composing, data are lined up at fast and afterward kept in touch with capacity during inactive machine cycles by the storing program or the drive controller. See cache coherency, compose back cache, compose through cache, pipeline burst cache, lookaside cache, inline cache, rear cache and NV cache.
Comments
Post a Comment